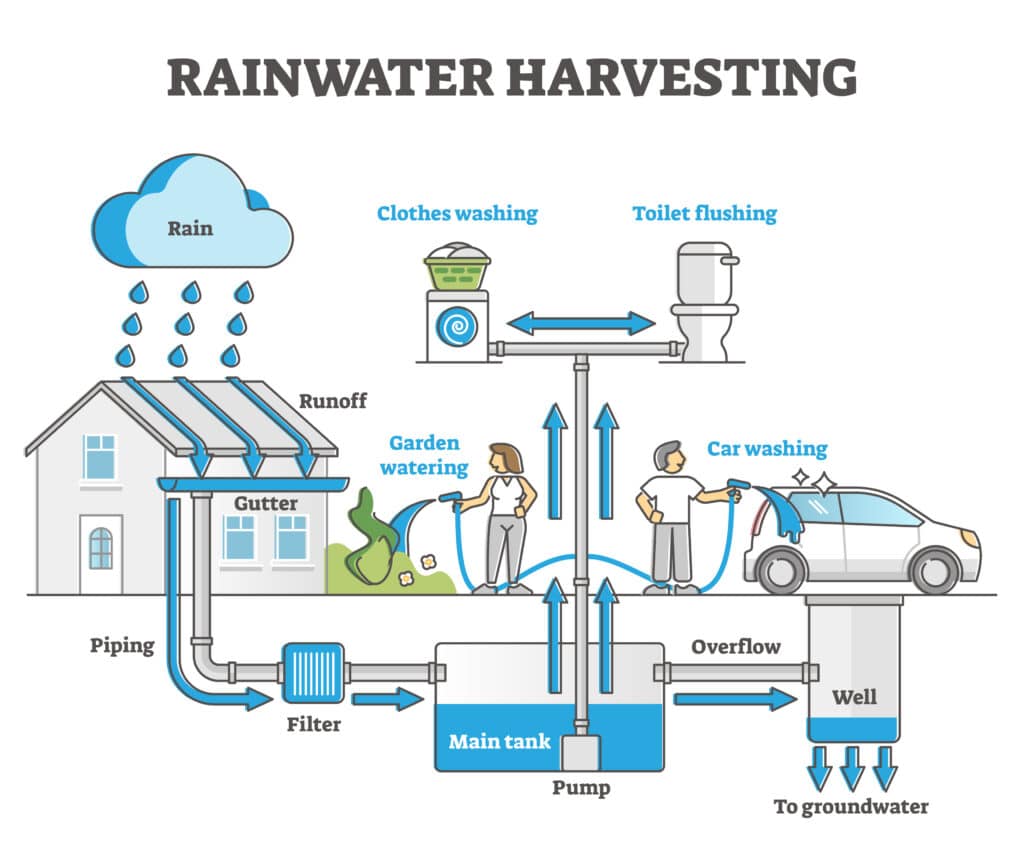
What are Rainwater Harvesting Systems?
Rainwater Harvesting Systems -Curious about using raindrops for more than just listening during a storm?
How about catching raindrops and using them to water your garden, wash your car, or even flush your toilets?
Well, that’s not just a fun thought—it’s possible with rainwater harvesting systems!
Let’s dive into how these amazing systems work and how they can benefit homes in Texas, especially in cities like Bedford, Euless, and Grapevine.
Understanding Rainwater Harvesting System
Rainwater harvesting systems are setups that collect, store, and use rainwater. They’re designed to catch rainwater from rooftops, direct it through gutters, filter out any debris, and store it in tanks for later use.
This process not only helps save money on water bills but also reduces the demand on our municipal water systems, making it a win-win for everyone.
In Texas, where the weather can swing from long dry spells to heavy rainfalls, managing water resources is crucial.
Cities like Bedford, Euless, and Grapevine can benefit significantly from these systems as they help cope with water restrictions during dry months and reduce runoff during heavy rains.
How Rainwater Harvesting Systems Work
Basic Components: Catchment, Conveyance, Storage
Rainwater harvesting systems are composed of three primary components that work together to collect and store rainwater for later use.
- Catchment Area: This is typically the roof of a building, which acts as the primary surface where rainwater is collected. The effectiveness of the catchment area can be influenced by its material and shape, affecting the quantity and quality of water collected.
- Conveyance System: This includes gutters and downspouts that channel the water from the roof to the storage area. The design of the conveyance system is crucial for maximizing water collection and minimizing blockages or leaks.
- Storage Tanks: These tanks hold the harvested rainwater until it is needed. They can vary greatly in size and material, depending on the intended use of the water and the space available. Proper placement and installation of these tanks ensure the longevity and efficiency of the water storage system.
The Water Collection Process
The process begins with rainwater hitting the catchment area and flowing into the conveyance system. Along the way, it passes through filters that remove leaves, insects, and other debris.
The first flush device diverts the initial dirty water that washes off the roof, preventing it from entering the storage tank.
The cleaner water follows, entering a storage tank where it is held until needed. This simple yet effective process ensures that the water stored is generally clean and less burdened with particulates.
Environmental Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting
Reducing Stormwater Runoff
Rainwater harvesting systems play a critical role in controlling stormwater runoff, a major cause of erosion and water pollution.
In urban areas, where concrete and asphalt cover much of the ground, rainwater often rushes into streets and drains, carrying pollutants into rivers and lakes.
By capturing rainwater from rooftops and other surfaces, these systems minimize this runoff, thereby protecting local waterways and reducing the burden on stormwater infrastructure.
Moreover, by limiting runoff, rainwater harvesting helps preserve topsoil and maintain the health of surrounding ecosystems.
Recharging Groundwater
One of the most significant benefits of rainwater harvesting is its ability to replenish local groundwater supplies, which are vital for drinking water, agriculture, and ecosystems.
In places like Texas, where water scarcity can be an issue due to periodic droughts and high usage, rainwater harvesting systems provide a sustainable source of water that percolates into the ground, slowly recharging aquifers.
This not only secures a supplementary water source during dry spells but also helps maintain the balance of the area’s natural hydrological cycles.
Mitigating Urban Heat Islands
Urban heat islands occur when cities experience higher temperatures than nearby rural areas due to human activities and concentrated energy usage.
Rainwater harvesting can mitigate this effect by providing a source of water for urban green spaces, gardens, and cooling systems.
Evaporation of this stored water cools the air, while vegetation uses it to create a cooler, more pleasant microclimate.
This not only makes urban environments more livable but also reduces the need for air conditioning, leading to lower energy consumption and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.

Photo from iStock – Credit: Anna Bergbauer
Economic Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting
Lowering Water Bills
Using harvested rainwater for irrigation, toilet flushing, and other non-potable uses can significantly reduce household water bills.
In regions with high water tariffs, the savings can be substantial, making rainwater harvesting a cost-effective solution for homeowners.
This reduction in municipal water demand also extends the life of existing water supply infrastructure and delays the need for new costly water supply and treatment facilities.
Reducing Demand on Municipal Systems
Rainwater harvesting reduces the strain on municipal water supply systems, especially during peak demand periods like the hot summer months.
By using harvested water for everyday needs, communities can lower their peak water usage, helping to stabilize local water supplies and ensuring that there is enough water available for all users.
This is particularly important in growing cities where water demand often outpaces supply.
Long-Term Cost Savings
Investing in rainwater harvesting systems can lead to significant long-term savings. While the initial setup cost might be substantial, the reduction in water bills and the potential for lower spending on water infrastructure maintenance can make it a financially sound investment over time.
Additionally, properties equipped with such systems may see an increase in market value, reflecting the growing demand for sustainable and self-sufficient homes.
Social Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting
Promoting Water Conservation
Rainwater harvesting systems highlight the importance of water conservation and resource management.
They serve as practical demonstrations of sustainable living, encouraging individuals and communities to consider how they use and manage natural resources.
By promoting water-saving practices, these systems help foster a culture of sustainability and responsible water use.
Enhancing Community Engagement
Community-based rainwater harvesting projects can strengthen community ties and foster a sense of cooperation among residents.
By working together to install, maintain, and benefit from these systems, community members develop a shared commitment to their local environment and collective well-being.
Such projects can also encourage local governance to adopt more sustainable practices and support similar initiatives.
Educational Opportunities
Educational institutions can use rainwater harvesting systems as a tool for teaching students about ecology, engineering, and sustainability.
These systems provide a tangible way to learn about the water cycle, water conservation, and climate change impacts. Furthermore, they inspire innovation and problem-solving as students consider how to optimize water usage and integrate sustainable practices into everyday life.
Schools and community centers become hubs of learning and engagement, where the practical benefits of sustainability are on display.

Photo from iStock – Credit: VectorMine
Types of Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting
This is the most common type and involves collecting rainwater directly from the roof surfaces of buildings.
It is particularly effective for residential settings where roof space is readily available and can be easily adapted to existing plumbing systems.
Additionally, rooftop systems are relatively simple to install and can be integrated with rain gutters and downspouts already in place.
Surface Runoff Harvesting
This method collects rainwater from land surfaces such as gardens, fields, or paved areas.
It is ideal for larger areas and is often used in agricultural settings or large residential complexes to manage excess water during heavy rains.
Surface runoff systems are crucial for controlling erosion and reducing the impact of runoff on local water bodies.
In-Situ Rainwater Harvesting
In-situ systems harvest rainwater directly where it falls. This could be through methods like building contour trenches in agricultural fields to capture runoff or using permeable pavements in urban settings that allow water to soak into the ground, aiding groundwater recharge directly.
These systems are especially beneficial in arid regions, helping to maximize water conservation and reduce the need for supplemental irrigation.
Choosing the Right Rainwater Harvesting System
Assessing Your Water Needs
Before choosing a system, it’s essential to evaluate how much water your household or business typically consumes for various needs such as irrigation, cleaning, and flushing toilets. This assessment helps determine the size and type of system required to meet your water demands efficiently.
Considering Local Climate and Rainfall
The effectiveness of rainwater harvesting systems largely depends on the local climate and rainfall patterns. Areas with high rainfall will benefit more, but even regions with lower rainfall can effectively use these systems with adequately sized storage tanks.
Evaluating Space and Budget Constraints
The physical space available for installing rainwater harvesting components and the budget are critical factors. Smaller properties might not accommodate large tanks, and budget constraints may limit the type of systems one can install.
Installation of Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Planning and Design Considerations
Effective rainwater harvesting requires careful planning to ensure that the system is tailored to the specific needs and conditions of the property. Key considerations include:
- Roof Structure Assessment: Evaluating the roof’s suitability for capturing rainwater, including its size, shape, and material. Consideration of the roof’s material and slope can significantly impact the efficiency of water collection.
- Tank Location: Determining the optimal placement for storage tanks to balance accessibility with aesthetic and practical property constraints. Strategic placement can also aid in gravity-fed systems, reducing the need for energy-intensive pumps.
- Component Compatibility: Ensuring that all parts of the system, such as gutters, downspouts, and tanks, work together efficiently. This includes matching the capacity of gutters and downspouts with the expected volume of rainwater to prevent overflows.
Steps for Installing a Basic System
Installation typically involves several detailed steps, each crucial for a successful setup:
- Gutter Setup: Installing gutters that are sloped properly to maximize water capture and minimize clogs. Properly aligned and secured gutters ensure optimal water flow to the storage tanks.
- First Flush and Filtration: Setting up first flush diverters to discard the initial dirty water and filters to clean the water before it enters the storage tanks. This step is vital for maintaining the purity of the stored water, making it suitable for various uses.
- Tank Connection: Securely connect the storage tanks to the gutters and ensure all joints are sealed to prevent leaks. Effective sealing techniques protect the quality of the water and the durability of the system.
Professional vs. DIY Installation
While some aspects of installation can be managed DIY, there are distinct advantages to professional installation:
- Professional Expertise: Professionals bring experience and knowledge of local regulations, ensuring the system is installed correctly and efficiently. They also bring insights into the best practices for system layout and component selection.
- Safety and Efficiency: A professional can safely integrate the system with existing plumbing and electrical setups, optimizing functionality and adherence to codes. Their experience also minimizes the risk of errors during installation, which can lead to costly repairs later.
- Long-term Support and Warranty: Professional installers often provide ongoing support and warranties for their work, giving homeowners peace of mind that any future issues will be resolved promptly. This support can be invaluable, especially for more complex systems that require regular maintenance and occasional troubleshooting.
Maintenance of Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Regular Cleaning and Inspection
Maintaining a rainwater harvesting system involves routine tasks to ensure its longevity and performance:
- Catchment and Conveyance Cleaning: Regularly clearing leaves and debris from gutters and the catchment area to prevent blockages. This routine maintenance ensures that the system remains efficient throughout the year.
- Tank Inspection and Cleaning: Periodically inspecting and cleaning storage tanks to prevent sediment buildup and microbial growth. Keeping tanks clean also prevents odors and maintains water quality.
- System Checkups: Conducting seasonal inspections to ensure all components are functioning correctly and making repairs as needed. These checkups help to extend the lifespan of the system and prevent minor issues from becoming major.
Preventing and Addressing Common Issues
Several issues could affect the performance of a rainwater harvesting system, and addressing them promptly is essential:
- Algae and Microbial Growth: Implementing solutions like opaque tanks and UV filters to inhibit growth. Regular monitoring and maintenance of these solutions are crucial to their effectiveness.
- Sediment Buildup: Installing sediment traps or additional filters to keep the storage water clean. These devices need to be checked and cleaned regularly to maintain their function.
- Mechanical Wear: Regularly replacing worn parts like washers and seals to maintain system integrity. Proactive maintenance of these components can prevent leaks and other problems associated with aging systems.
Ensuring Water Quality and Safety
For systems intended for potable use, maintaining water quality is critical:
- Regular Water Testing: Conducting water quality tests to detect contaminants and ensure safety. This helps in adjusting filtration and disinfection protocols as needed.
- Filtration and Disinfection: Utilizing multi-stage filtration and disinfection processes to meet drinking water standards. This often includes mechanical, chemical, and biological treatment processes.
- System Upgrades: Keeping the system updated with the latest technology to enhance safety and efficiency. Upgrades can include new filtration technologies or smarter control systems for more efficient water management.
This comprehensive approach to understanding, choosing, installing, and maintaining rainwater harvesting systems ensures they provide a reliable and sustainable water supply while promoting conservation and reducing utility costs.
Conclusion: Harvesting Rain, Reaping Benefits
Rainwater harvesting systems offer a wealth of advantages, making them a superb choice for enhancing the sustainability of homes across Texas, including cities like Bedford, Euless, and Grapevine.
By adopting these systems, homeowners can significantly reduce their water bills and contribute positively to environmental conservation.
Additionally, rainwater harvesting encourages a more self-sufficient lifestyle, reducing dependence on municipal water supplies and ensuring a resilient water source during dry spells.
FAQs
What are rainwater harvesting systems and how do they work?
Rainwater harvesting systems are setups that collect, store, and utilize rainwater from surfaces like rooftops. These systems typically include a catchment area, conveyance system, storage tanks, filtration units, and distribution systems to supply harvested water for various uses.
Can rainwater harvesting systems reduce my utility bills?
Yes, rainwater harvesting systems can significantly reduce your water bills by providing a supplementary water source for non-potable uses such as irrigation, flushing toilets, and washing cars, thereby decreasing your dependence on municipal water supplies.
Are rainwater harvesting systems environmentally beneficial?
Rainwater harvesting systems play a crucial role in sustainable water management. By capturing and utilizing rainwater, these systems reduce runoff, lower the demand on municipal water systems, and help in recharging the local groundwater.
What is the maintenance requirement for rainwater harvesting systems?
Maintaining rainwater harvesting systems involves regular cleaning of gutters and filters, inspecting storage tanks for sediment build-up, and ensuring all components are functioning properly to maintain water quality and system efficiency.
How do I choose the right size for my rainwater harvesting system?
Choosing the correct size for your rainwater harvesting system depends on several factors including the roof area available for collecting rainwater, the average rainfall in your area, and your water usage needs. It’s often best to consult with professionals to assess these factors and design a system that meets your specific requirements.
What legal considerations should I be aware of before installing a rainwater harvesting system?
Before installing a rainwater harvesting system, it is important to check with local authorities for any specific regulations or permits required in your area. Compliance with local building codes and environmental regulations is crucial to ensure that your system is not only effective but also legally sound. In some regions, incentives or rebates might be available to encourage rainwater harvesting, which can offset some installation costs.


